Cloud Cost Management
Cloud cost management involves monitoring and controlling the expenses associated with using cloud services. It includes practices such as setting budgets, tracking spending, and identifying areas where costs can be reduced. Cloud cost management is focused on ensuring that organizations are using cloud resources efficiently and effectively while staying within budget.
Cloud cost monitoring is focused on tracking and analyzing cloud costs, both are important for effective cloud cost management and can help organizations save money and improve their overall cloud performance.
Cloud Cost Optimization
Cloud cost optimization is about maximizing the value that an organization gets from its cloud spending. This involves identifying ways to reduce costs while also improving performance, scalability, and reliability. Cloud cost optimization may include practices such as rightsizing resources, using reserved or spot instances, and using automation to manage resources more effectively.
Cloud cost optimization is a combination of strategies, techniques, best practices, and tools that not only help reduce cloud costs but also maximize the business value of using the cloud.
It involves enhancing cloud cost efficiency by identifying and reducing mismanaged or excess resources, taking advantage of discounts to reserve higher capacity, and rightsizing computing resources to specific applications and workloads in the cloud environment.
Optimizing cloud costs isn’t just about reducing costs; it’s also about aligning costs with business goals.
The relationship between cloud cost monitoring and cloud cost optimization is that monitoring provides the data and insights necessary to make informed decisions about cost optimization. By monitoring cloud usage and costs, organizations can identify areas where they can save money, such as unused resources, overprovisioning, or inefficient usage patterns. With this information, they can then take action to optimize their cloud costs by implementing strategies to reduce waste and improve efficiency.
In summary, cloud cost management is about controlling costs and staying within budget, while cloud cost optimization is about optimizing costs to maximize value and improve overall performance.
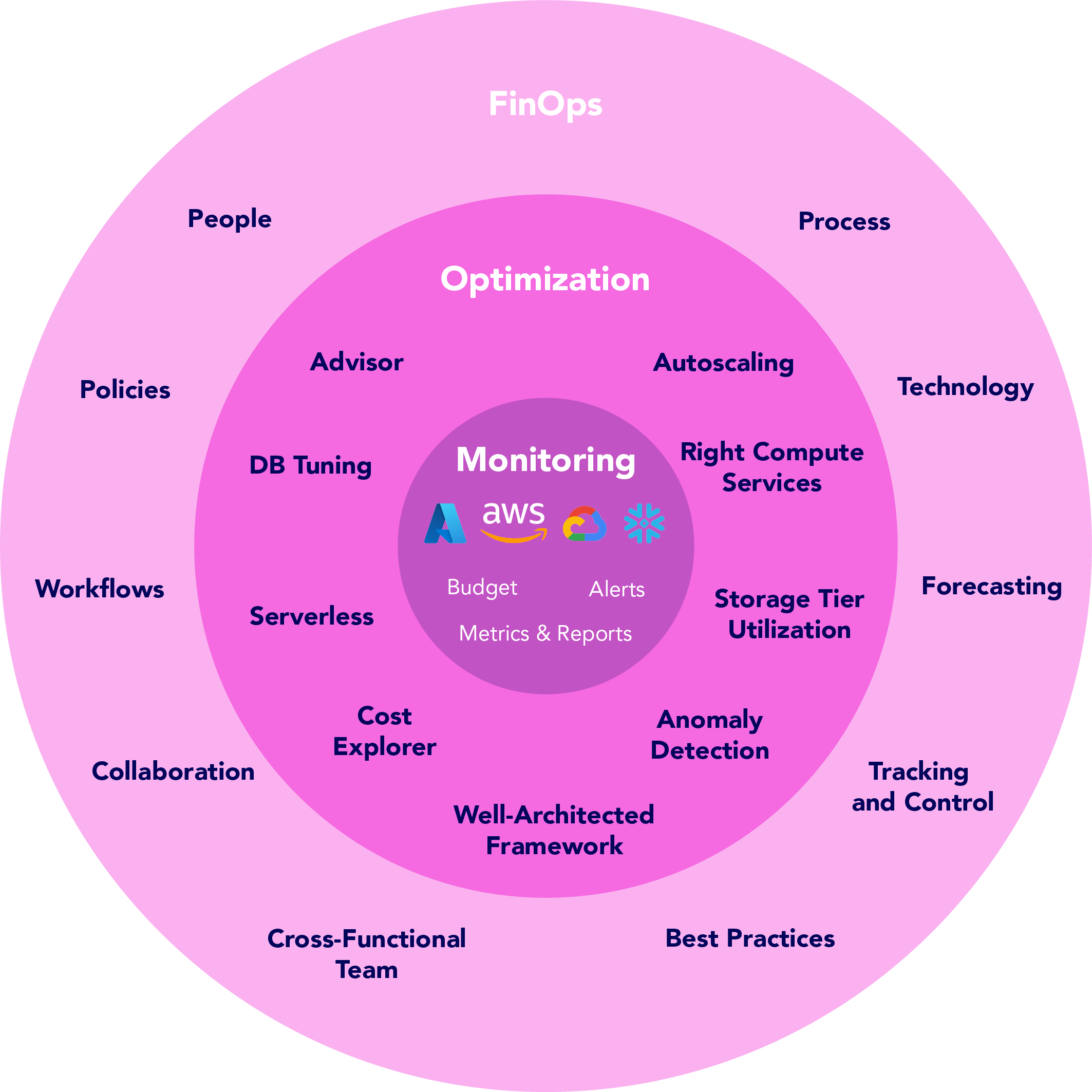
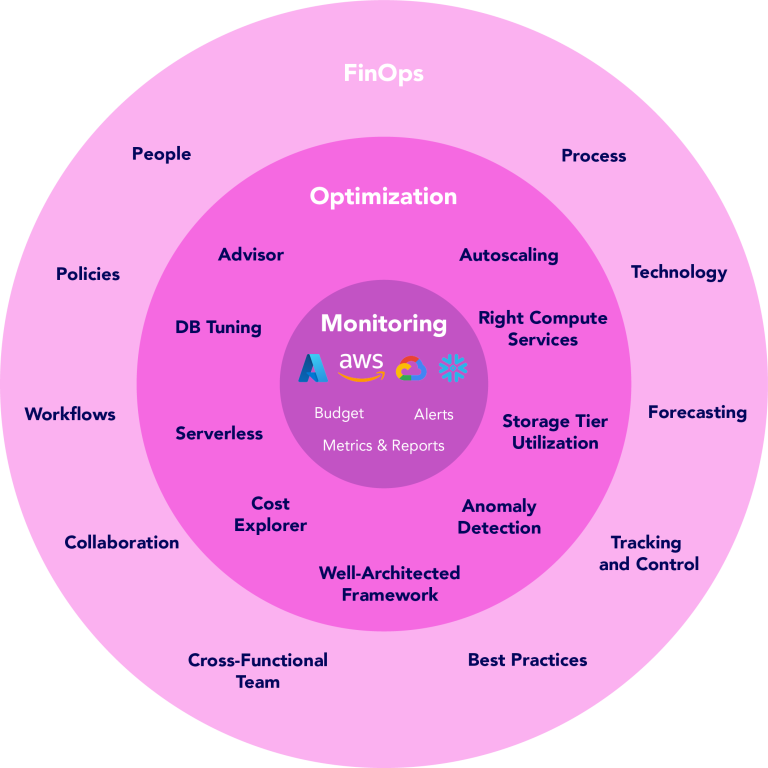
FinOps
FinOps (Financial Operations) is a practice of cloud financial management that emphasizes cloud cost optimization as a key aspect of effective cloud management. It provides a framework for managing and optimizing cloud costs by bringing together cross-functional teams, establishing clear processes and workflows, and leveraging tools and technologies for cloud cost optimization.
The focus of FinOps is optimizing cloud costs by bringing together cloud, finance, and business teams to manage and optimize cloud spending. It is a framework that enables organizations to manage their cloud costs effectively by providing a set of best practices, tools, and processes for cloud cost optimization.
FinOps involves three key elements: people, process, and technology. The people element involves collaboration between cross-functional teams, such as cloud operations, finance, and business units. The process element involves establishing clear policies, procedures, and workflows for managing cloud costs, such as budgeting, forecasting, and tracking costs. The technology element involves leveraging tools and technologies for monitoring, analyzing, and optimizing cloud costs.
Cloud cost optimization is a key aspect of FinOps, as it involves taking action to reduce or optimize cloud costs. FinOps provides a structured approach to cloud cost optimization by providing a set of best practices and tools for monitoring and managing cloud costs.
By adopting FinOps practices, organizations can gain greater visibility into their cloud costs and usage, identify cost-saving opportunities, and implement strategies to optimize cloud spending. This can result in significant cost savings and improved operational efficiency, as well as better alignment between cloud usage and business goals.
Relationship Between FinOps Cloud Cost Optimization and Cloud Cost Management
Best Practices for Cloud Cost Optimization
- Become familiar with cloud provider billing and cost management tools.
- Implement cost alerts.
- Set up budget and allocate cost.
- Choose the right compute service.
- Be aware of anomaly detection.
- Understand autoscaling pros and cons.
- Optimize to pay only for the compute you need.
– Identify idle VMs and storage.
– Schedule VM to auto stop.
– Right-size VMs.
– Leverage reserved and spot VMs.
– Implement autoscaling according to best practices.
– Review and implement recommendations from advisor tools.
- Optimize Cloud Storage costs and performance.
– Storage class.
– Lifecycle policies.
– Review and delete duplicate data.
- Tune your databases and data warehouses.
- Filter network packets
- Identify top consumers.
- Select right network tiers.
AWS Cloud Cost Optimization Tools
AWS Cost Explorer: cost management tool that allows you to view, analyze, and manage AWS costs and usage. Visualize your AWS cost and usage data, identify cost drivers, and create custom reports.
AWS Budgets: cost monitoring tool that allows you to set custom cost and usage budgets for AWS resources. Track your spending against budget, receive alerts when you exceed budget, and adjust resources as needed.
AWS Trusted Advisor: tool that provides recommendations for optimizing AWS resources for cost savings, security, and performance. Identify cost optimization opportunities and implement best practices for cost-effective use of AWS resources.
AWS Cost Anomaly Detection: machine learning-powered tool that analyzes AWS cost and usage data to detect anomalies and unusual patterns. Identify cost spikes, unexpected usage, and other anomalies that may indicate cost optimization opportunities or security issues.
AWS Cost and Usage Reports: provide detailed billing and usage data for AWS resources. Analyze your usage patterns, identify cost drivers, and optimize resource usage for cost savings.
Spot Instances: The AWS EC2 compute instances acquired by bidding on unused EC2 instances. Spot Instances are generally much cheaper than on-demand instances.
Auto Scaling: AWS service that allows automatic adjustment of the number of EC2 instances per workload. Helps maintain application availability and optimize resource usage.
Azure Cost Optimization Tools
Azure Cost Management and Billing: free tool that provides cost analytics, cost forecasting, and cost alerts to help manage cloud costs effectively. Track and analyze spending across different Azure services and receive recommendations for cost optimization.
Azure Reservations: prepay for Azure services such as virtual machines for one or three years at a discounted rate. Save up to 72% on Azure costs compared to pay-as-you-go pricing.
Azure Spot Virtual Machines: take advantage of unused Azure capacity at a significantly lower cost. Run workloads on Azure Spot Virtual Machines for as long as the capacity is available, and you pay spot price, which is often significantly lower than the on-demand price.
Azure Auto Scaling: automatically adjust the number of virtual machines running your workload based on demand. This can help optimize resource usage and reduce overall cloud costs by only running the resources you need when you need them.
Azure Advisor: free tool that provides personalized recommendations for optimizing Azure resources. Analyzes resource usage and provides recommendations for cost optimization, security, and performance.
Optimize your Azure Resource Configuration: optimizing resource configuration, such as virtual machine size and storage options, can help reduce cloud costs. For example, using smaller virtual machine sizes or changing storage to less expensive options can significantly reduce overall cloud costs.
Azure Savings Plan: provide a flexible and cost-effective way for customers to purchase Azure services. The discounts customers receive depend on the specific Savings Plan and upfront payment.
Azure Hybrid Benefit: enables customers to use their current, on-premises Microsoft services licenses for corresponding Azure services. It provides customers with a flexible, cost-effective way to extend their on-premises investments to the cloud.
Azure Pricing Calculator: tool provided by Microsoft to estimate the cost of using various Azure services.
Google Cloud Cost Optimization Tools
Google Cloud Billing: provides visibility into Google Cloud costs, usage, and budget information. Customers can view detailed usage reports, set budget alerts, and analyze costs to optimize spending.
Google Cloud Cost Management: provides centralized view of cloud costs across multiple projects and services. Track and analyze costs, identify trends and patterns, and generate custom reports.
Google Cloud Operations Suite: includes Cloud Monitoring, Cloud Logging, and Cloud Trace, which can help optimize cloud performance and reduce costs by identifying and resolving issues quickly.
Google Cloud AutoML: machine learning tool to automatically optimize Google Cloud resources and reduce costs. Automatically scales resources based on usage and demand and provides recommendations for cost savings.
Google Cloud Functions: optimize cloud costs by running code only when necessary.
Google Cloud Storage: cost-effective way to store and access data in Google Cloud. Customers can use storage classes to manage the cost of storing data based on access patterns and use lifecycle management to automatically move data to cheaper storage options over time.
References
Google, Azure, Amazon, Gartner, Cloudzero