AWS, a pioneer in cloud computing, offers a suite of services that together form a robust Modern Data Platform. This platform not only addresses the challenges of big data but also provides tools for advanced analytics, machine learning, and real-time processing.
The AWS Modern Data Architecture
The AWS Modern Data Architecture is a layered approach to data management.
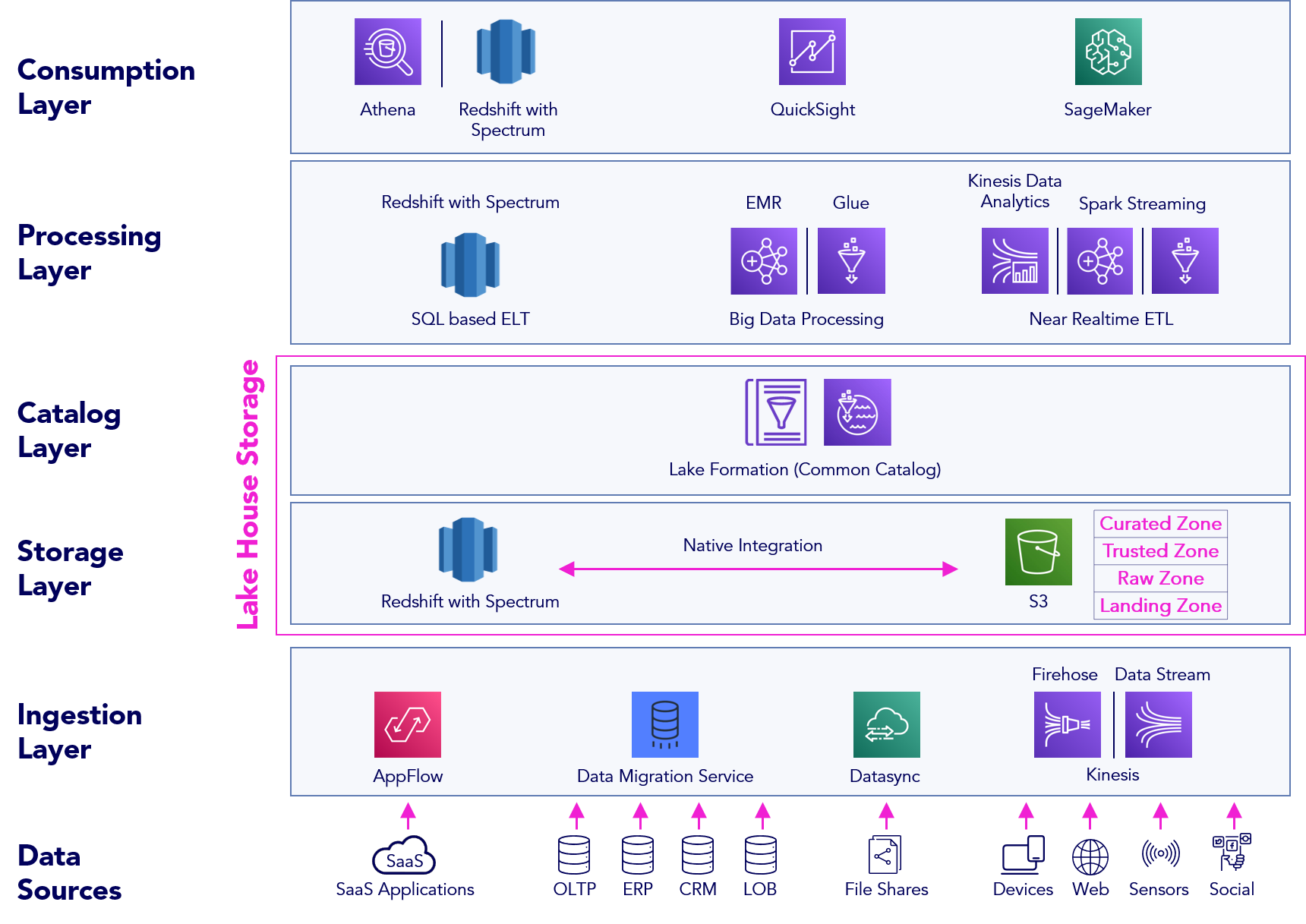
It encompasses six distinct layers:
- Data Sources: The origin of all data, encompassing a variety of formats and structures.
- Ingestion Layer: Tools like AppFlow, Data Migration Service, Data Sync, Firehose, and Kinesis Data Streams ensure seamless data intake.
- Storage Layer: Amazon S3 acts as the backbone and is segmented into:
Landing Zone – The initial resting place for raw, unprocessed data.
Raw Zone – Data undergoes preliminary processing, making it more structured.
Trusted Zone – Data is further refined, cleaned, and enriched.
Curated Zone – The final zone where data is optimized for analytics and reporting. - Catalog Layer: AWS Lake Formation ensures data is cataloged, discoverable, and accessible.
- Processing Layer: Incorporates SQL-based ELT with tools like AWS Glue, big data processing with EMR, and real-time processing using Kinesis Data Analytics and Spark Streaming.
- Consumption Layer: Athena, Redshift with Spectrum, Quicksight, and SageMaker facilitate data consumption and analytics.
Architectural Flow
Data typically flows from various sources into the AWS ecosystem. It lands in the Landing zone, where it remains in its raw form. Through AWS Glue, it undergoes transformations, moving from the Raw zone to the Trusted zone. Post transformation, data is either moved to Redshift for complex analytics, forming the Curated zone, or is processed in real-time through Lambda and Kinesis.
AWS Services
Amazon S3: At the heart of the platform is Amazon S3, providing scalable and secure data storage. It acts as the primary data lake, accommodating the Landing and the Raw zone.
AWS Glue: Beyond storage, data needs to be discoverable and accessible. AWS Glue offers data cataloging capabilities, ensuring that datasets are easily found. Additionally, its ETL functionalities transform raw data, transitioning it from the Trusted to the Curated zone.
Amazon Redshift Spectrum: Extends Amazon Redshift’s capabilities for complex queries across large datasets. This data warehousing solution is optimized for online analytic processing (OLAP), making it a cornerstone for the Curated zone.
AWS Lambda and Amazon Kinesis: Real-time data processing is crucial for many modern applications. AWS Lambda offers serverless computing, allowing for immediate data processing as soon as it lands in S3. In tandem, Amazon Kinesis captures real-time data streams, ensuring that the platform can handle both batch and real-time data.
Amazon Athena: For ad-hoc querying, especially directly on the data lake (S3), Athena provides a serverless interface. It allows for immediate insights without the need for complex ETL jobs or even moving the data.
Advantages of AWS’s Approach
The AWS Modern Data Platform is not just about storing data; it’s about making data actionable. The tight integration of services ensures that data moves seamlessly through the layers, transforming from raw information to actionable insights. The platform’s scalability ensures that it can handle petabytes of data, while its flexibility means it can adapt to ever-changing business needs. Moreover, AWS’s commitment to security ensures that data remains protected at all times.

