


Leverage our innovations and investments as your Cloud Squadron.
Conquer the chronic challenges of security, cost, uninterrupted uptime, and low network latency.
Continuously optimize and expand your Cloud based capabilities.
Balance flexibility with performance without sacrificing scalability.
The diverse needs of applications can be better met by a mix of environments. What should you consider?
Curate the Data that matters.
A Data Warehouse should only contain curated data that is core to keep your business running.
Stop the sprawl. Integrate the silos. Come together.
On the Cloud you are still responsible for user authentication and authorization, identity management, data encryption, and access control to protect data. Our proSkale Consultants can check for these issues and more:
Cloud costs are underestimated by an average of 23%. Moving to the Cloud often excludes the necessary monitoring and oversight. Cloud costs can quickly get out of hand without visibility on use and performance. Our Cloud Squadron solutions can:
Assess Readiness – Our solutions and expertise can quickly assess your readiness for new or expanded Cloud capabilities.
Map it out – Your journey includes:
Design the Architecture – Our Cloud Squadron brings the experience and solutions to design a world class infrastructure. Don’t do it alone.
It is very time-consuming and expensive to build Cloud migration expertise in house that you may only use once. Don’t wait – SKALE UP!
proSkale’s Cloud Squadron have the solutions to complete your migration successfully. We have an array of tools that:
Don’t forget – Cloud migrations are also a great opportunity to expand automation.
Start simple and move on to more complex applications.
Remember – Integration with on-prem Legacy applications will always take longer than planned.
Security! Create a clear Cloud security model and policies before you migrate.
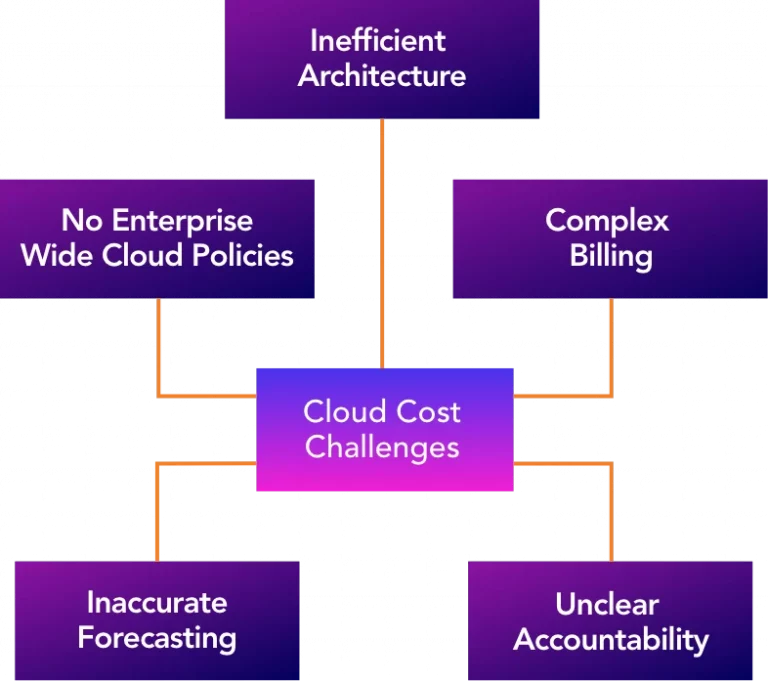
Bringing all Cloud costs across the enterprise under control is the top Cloud priority for 74% of all organizations. And with good reasons. The ease of using the Cloud can unintentionally drive up costs beyond your budget. The complexity of Cloud Architectures can make optimization challenging.
Cloud Management is much more than a technical exercise. It is a continuous activity to optimize operations, costs, and value generation.
Our Cloud Squadron will give you the visibility and advice you need. Optimization is not limited to managing cloud costs alone. If you are experiencing one or more Cloud cost challenges, our expert proSkalers are ready to deploy the solutions you need to optimize your Cloud and continuously maintain optimal operations.
Pros of on-premise
Cons of on-premise
Pros of public cloud
Cons of public cloud
Pros of multi-cloud
Cons of multi-cloud
All your Corporate reporting and dashboards should be using the Data Warehouse as their source of data, especially if they are related to performance or financial incentives. If your employees’ performance is being measured on spreadsheets and not from data in the Data Warehouse – no one will care what is in the Data Warehouse.
Almost half of companies report their data management and warehouse processes were being done manually, consuming valuable time, resources, and money. If loading the data is slow, difficult and delayed – no one will use the Data Warehouse. SKALE UP and automate these processes.
A Data Warehouse is also not a dumping ground. Nearly half (48%) of the data migrated into Data Warehouses requires cleaning before it could be useful. This is more than four hours of time lost per knowledge worker each week to work on missing data, duplicate data, or data that needed reformatting. SKALE UP – a robust Data Governance program will quickly and efficiently curate data for the Data Warehouse.
The concept of Data Lakes emerged in response to what was seen as the shortcomings of Data Warehouses such as:
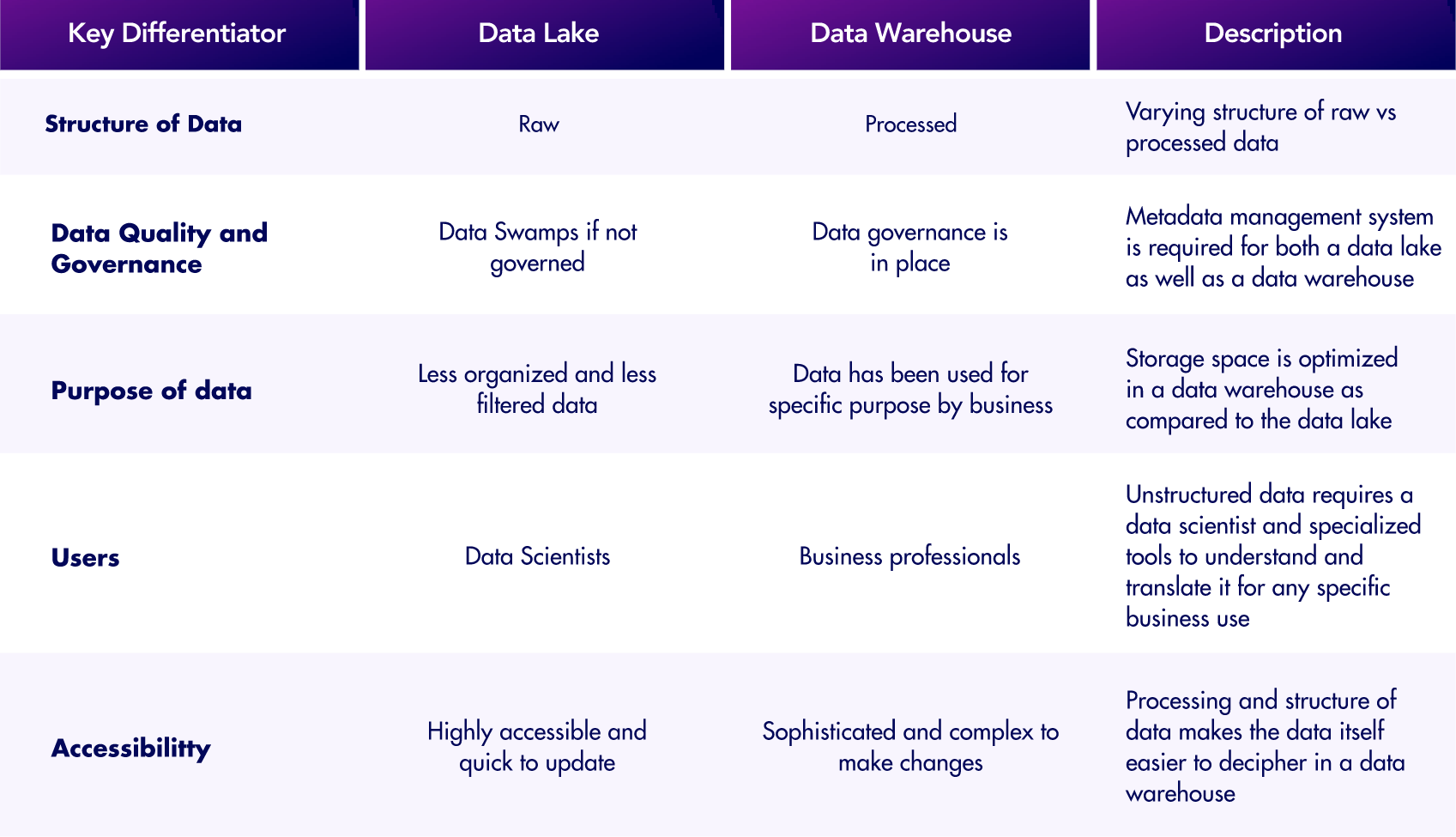
Raw data is loaded into the Data Lake without transformation, unstructured and structured data can be experimented upon by Data Scientists to find new insights.
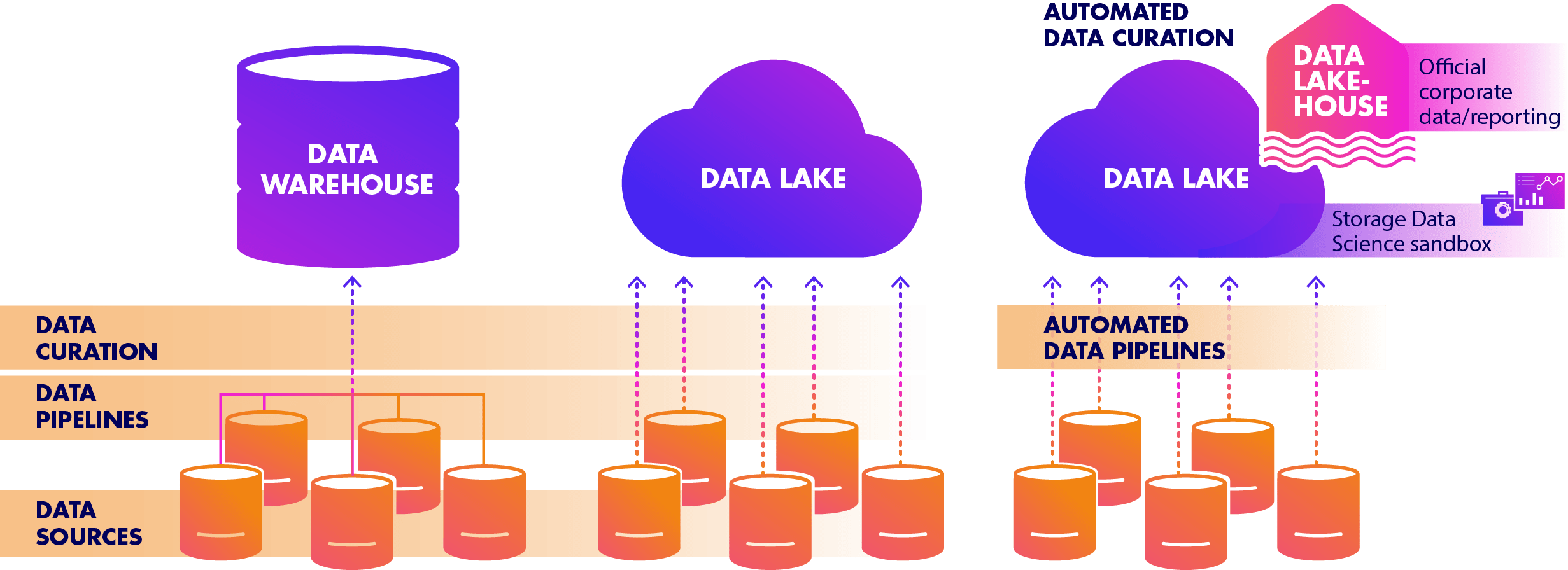
The next evolution is the Data Lakehouse – combining the best of the Data Warehouse and Data Lake. Properly structured Lakehouse data is the source for official KPI’s, reports and dashboards for the entire Enterprise.
proSkalers can rapidly transform your Data Warehouse and Data Lake to a Data Lakehouse to scale your reporting and Data Science capabilities. Reduce the drain on resources by automating Data Pipelines, Data Preparation and corporate reporting.
You’re only 2 weeks away from a completely tailored baseline infrastructure, one that empowers you to scale, not creates more dependencies.
Many organizations are moving their on-prem IT infrastructure and functions to Cloud as part of their IT strategy. There are several reasons for moving to Cloud: reduced cost, operationalization of fixed cost, faster time-to-market, flexibility, scalability, robust business continuity, increased security, controls and governance and availability of variety of software services for Infrastructure as Service (IaaS), Platform as Service (PaaS) and Software as Service (SaaS).
Microsoft has established itself as a dependable business partner and its products are already being used in a large number of on-prem IT environments. Some of the most popular Microsoft products include Active Directory, SQL Server, SharePoint, and Office products, such as MS Work, Excel, PowerPoint, Outlook, PowerBI, etc.
A Microsoft Azure environment meshes seamlessly with other Microsoft products that are already in use on-premises, so migration of these products and services to Azure is much easier than creating and using similar types of new products.
Many Microsoft products already integrate extremely well with several popular SaaS (Software as a Service) services like ServiceNow, WorkDay, Salesforce, Adobe, etc., and migration to Azure carries the integration layer with little change. Moving to the Azure environment requires only small configuration changes for these products due to change in IP addresses, port numbers etc. Since Azure Active Directory is similar to the existing on-prem Active Directory, the user authentication and authorization process remain more-or-less the same, reducing the need to retrain staff.
Microsoft has a large partner network on Azure; these partners provide Azure-based digital products in almost all computing areas. If a product or service you need is not available in Azure, it’s likely available through a Microsoft partner network in Azure Marketplace.
A Modern Data Platform on Azure provides one single view of enterprise data by providing centralized storage in a Data Lake, several automated and powerful tools such as Azure Data Factory (ADF), Spark-based Databricks environment for transformation, Synapse analytics data warehouse, Azure Event Hub, Azure Stream Analytics, Azure Analytics Services, containers, Kubernetes services, integration of Github and almost all open source Apache data products. The Modern Data Platform uses Gamma architecture to support both batch and stream processing and consumptions. The Azure Cosmos DB provides capability for storing NoSQL data for consumption by APIs in real time.




Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services—including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the Internet (“the cloud”) to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale.
Cloud computing allows companies to rent the required infrastructure they need to operate instead of owning it. This allows for companies to cut upfront cost and only pay for the storage and analytics they use.
The cloud provides a number of IT services such as servers, databases, software, virtual storage, and networking, among others. In simple terms, Cloud Computing is defined as a virtual platform that allows you to store and access your data over the internet without any limitations.
There are also 3 main types of cloud computing services: Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platforms-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS).
The main benefits include a cost-saving pay as you go structure, a flexible structure that can grow with you, and access to a multitude of options for infrastructure.
While cloud computing can increase flexibility and cost efficacy, you rely on an network-based system, so if there are local or datacenter outages, companies may temporarily lose access to the cloud.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
Cloud migration refers to transferring your data infrastructure to the cloud.
The process of moving digital business operations into the cloud.
The cloud allows for faster delivery times, creates room for innovation, lowers total cost ownership (TCO), and increases the flexibility and agility of your infrastructure.
The main challenges seen when migrating to the cloud are migration complexity, cloud management, rebuilding applications and ease of modernizing from legacy applications.
The cloud migration process has three main steps: strategy building, research and assessment, and cloud migration.
There are three types of cloud migration: Re-host, which moves applications from on-site to the cloud; Re-platform, which moves your applications to new operating systems; and Re-factor, which updates current components to fit company needs.
The main tools used in cloud migration are Amazon Web Service (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
For AWS – AWS Migration Services. AES migration services, CloudEndure, TSO Logic, AWS Migration Acceleration Program.
For Azure – Azure Database Migration Service, Movere for Assess servers, Azure Data Box to Migrate offline data.
For GCP – Google Cloud Storage Transfer Service, Google BigQuery Data Transfer Service, Cloud Sprint.
Cloud service providers are third parties that help companies facilitate and manage cloud computing services.
The main reasons for using a cloud provider are security in your infrastructure, eliminating costs, and accessibility to a variety of platforms and software.
Using a cloud provider is a helpful way to access computing services that you would otherwise have to provide on your own, such as Infrastructure.
To pick a cloud provider, it is important to evaluate key factors like needs, business goals, current infrastructure, and requirements. Then, when picking a provider, ensure their infrastructure meets your requirements and can support your goals.
Check cloud provider Certifications & Standards, Technologies & Service Roadmap, Data Security, Data Governance and Business policies, Service Dependencies & Partnerships, Reliability & Performance.
Cloud infrastructure is the components required for cloud computing, like storage hardware and network resources.
Using abstraction tools like virtualization, cloud infrastructure separates information and resources from hardware and brings them to the cloud.
It includes hardware, abstracted resources, storage, and network resources.
The components of cloud infrastructure are hardware, virtualization, network, and storage.
Cloud transformation is the process of migrating infrastructure from hardware to the cloud.
Cloud transformation increases efficiency, lowers cost, and improves scalability.
The issues companies most often have to overcome with cloud computing are compliance with company or government regulations, the complexity of the migration process, lack of expertise with evolving technology, and increased cybersecurity measures.